Every dog owner knows that their furry friend’s health is a top priority. One often overlooked aspect of canine care involves the anal gland. These small sacs, located on either side of the anus, play a crucial role in your pet’s well-being. Normally, they are expressed naturally during bowel movements, but sometimes, issues arise.
When the gland becomes full, it can lead to discomfort and even more severe health problems. Recognizing the signs early can prevent complications. Symptoms like scooting, excessive licking, or a foul odor are common indicators. Understanding these signs is essential for maintaining your pet’s overall wellness.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about anal gland issues. From identifying symptoms to preventive measures, you’ll gain the knowledge to keep your dog happy and healthy. Stay tuned for actionable tips and expert advice.
Key Takeaways
- Anal glands are small sacs located on either side of a dog’s anus.
- Full glands can cause discomfort and health issues if not addressed.
- Common signs include scooting, excessive licking, and foul odor.
- Regular monitoring can prevent complications.
- This guide provides detailed insights into identifying and managing gland problems.
Understanding Dog Anal Glands
Dog anal glands are a vital yet often misunderstood part of canine anatomy. These small, pea-sized sacs are located on either side of the anus and play a crucial role in your pet’s health. Each gland is connected to the rectum via small tubes, allowing for the release of fluid during specific activities.
What Are Anal Glands?
Anal glands, also referred to as anal sacs, are specialized structures in dogs. They produce a unique fluid that is typically expelled during bowel movements. This fluid serves as a form of scent marking, helping dogs communicate with one another. Understanding their anatomy is key to recognizing when something is wrong.
These sacs are naturally expressed when a dog defecates. The pressure from the stool helps release the fluid, preventing buildup. However, if this process is disrupted, it can lead to discomfort or more serious issues.
How Anal Glands Function During Bowel Movements
During a bowel movement, the pressure from the stool compresses the anal glands, causing them to release their contents. This natural expression is a built-in mechanism to avoid impaction. Regular bowel movements are essential for maintaining gland health.
When this process fails, symptoms like scooting or excessive licking may occur. Recognizing these signs early can prevent complications. Below is a summary of key points about anal glands:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | On either side of the anus |
| Size | Pea-sized sacs |
| Function | Fluid release during bowel movements |
| Role | Scent marking and communication |
| Common Issues | Impaction, infection, or abscess |
“The natural expression of anal glands during defecation is a critical process for maintaining canine health.”
Understanding the normal function of anal glands is essential for recognizing abnormalities. By staying informed, you can ensure your dog remains healthy and comfortable.
Signs Your Dog’s Anal Glands Are Full
Behavioral changes in your dog may signal issues with their anal glands. These small sacs, located near the anus, can cause significant discomfort when full. Recognizing the signs early can prevent more serious problems.
Behavioral Symptoms to Watch For
One of the most common signs of full anal glands is scooting. This behavior, where your dog drags their rear across the floor, is often a clear indicator of discomfort. Excessive licking or biting around the anal area is another red flag. These actions suggest your pet is trying to relieve pain or irritation.
Other behavioral changes include restlessness or difficulty sitting comfortably. If your dog seems unusually agitated or is avoiding certain activities, it could be due to anal gland issues. Paying attention to these subtle signs can help you address the problem before it worsens.
Physical Indicators and Odor Issues
Physical symptoms are equally important to monitor. Swelling or redness around the anus may indicate full or impacted glands. Discomfort during defecation is another common sign, as the pressure from stool can exacerbate the issue.
A strong, fishy odor is a telltale sign of anal gland problems. This distinct smell is caused by the fluid released from the glands. If you notice this odor, it’s a clear signal that your dog needs attention. Persistent symptoms should prompt a visit to the vet to prevent complications.
“Early detection of anal gland issues can save your dog from unnecessary pain and discomfort.”
Regular monitoring of your dog’s behavior and physical condition is essential. By staying vigilant, you can ensure your pet remains healthy and comfortable. Addressing these signs promptly can prevent minor issues from escalating into serious health problems.
How to tell if dogs anal glands are full
Monitoring your dog’s health includes paying attention to subtle changes in their behavior and physical condition. One area that often requires careful observation is the anal gland. These small sacs can cause discomfort when full, and early detection is key to preventing complications.
Performing a Visual Inspection
To check for signs of fullness, gently examine your dog’s anal area. Look for swelling, redness, or discharge. These physical changes may indicate that the gland is not emptying properly. Always handle your pet with care to avoid causing discomfort.
If you notice any abnormalities, compare them to your dog’s normal appearance. Sudden changes, such as excessive licking or scooting, should be noted. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating.
Understanding Stool Consistency
Stool consistency plays a significant role in gland expression. Firm stools apply the necessary pressure to naturally empty the glands during bowel movements. Soft stools, on the other hand, may not provide enough pressure, leading to buildup.
If your dog frequently has soft stool, it could be a sign that the glands are not being expressed naturally. Dietary adjustments, such as adding fiber, can help firm up the stool and promote healthy gland function.
“Regular monitoring of stool consistency and anal area health is essential for preventing gland-related issues.”
When performing inspections, always prioritize your dog’s comfort. If you’re unsure about what you’re seeing or if symptoms persist, consult your veterinarian. They can provide professional guidance and ensure your pet’s well-being.
Anal Gland Impaction and Infection Overview
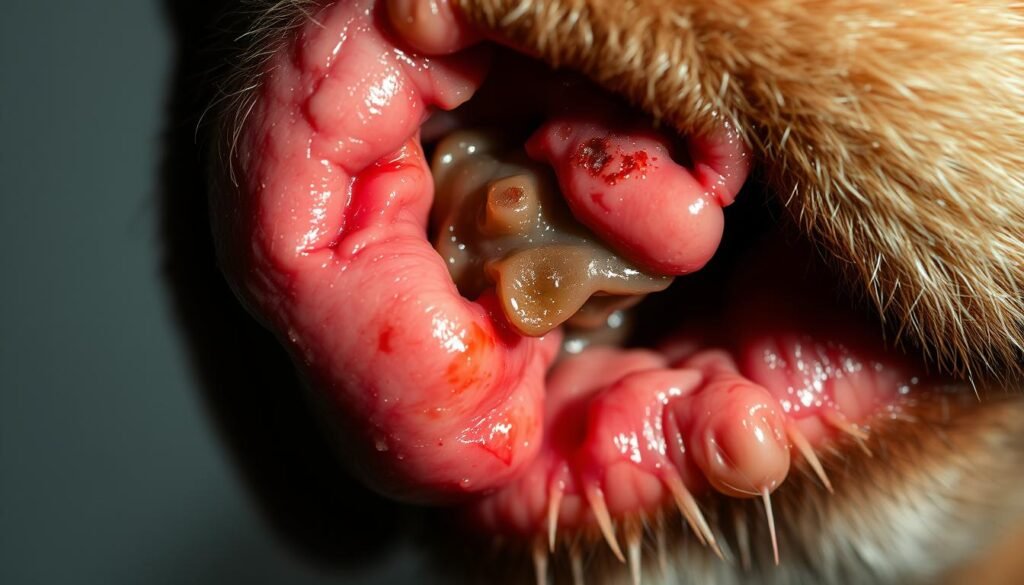
Anal gland issues in dogs can escalate quickly if left untreated, leading to severe discomfort and health complications. These small sacs, located near the anus, play a vital role in your pet’s well-being. When they become impacted or infected, the consequences can be painful and potentially dangerous.
Causes and Symptoms of Impaction
Impaction occurs when the liquid inside the anal gland thickens, preventing natural expression. This buildup can result from changes in stool consistency, such as soft stools that fail to apply enough pressure. Other contributing factors include obesity, chronic skin dermatitis, and insufficient dietary fiber.
Common symptoms of impaction include scooting, excessive licking, and discomfort during defecation. Swelling or redness around the anal area may also be present. Early detection is crucial to prevent further complications.
Identifying Signs of Infection or Abscess
If impaction is left untreated, it can progress to infection or abscess formation. Infected glands often exhibit redness, swelling, and a foul odor. Your dog may experience severe pain and show signs of restlessness or agitation.
In advanced cases, the sac may rupture, leading to further complications. Inflammation and a buildup of pus are clear indicators of an abscess. Immediate veterinary attention is essential to manage these conditions effectively.
“Untreated anal gland issues can lead to serious health problems, making early intervention critical.”
Understanding the causes and symptoms of impaction and infection is key to maintaining your dog’s health. Regular monitoring and prompt action can prevent minor issues from becoming major concerns.
When to Visit a Veterinarian
Knowing when to seek professional help for your dog’s health is crucial for their well-being. While some issues can be managed at home, others require immediate veterinary attention. Recognizing the signs that indicate a problem with your dog’s glands can prevent complications and ensure timely treatment.
Recognizing Red Flags in Your Dog’s Behavior
Certain behaviors in your dog should raise concern. Persistent scooting, excessive licking, or biting around the anal area are clear indicators of discomfort. These actions often suggest that the glands are not functioning properly and may be impacted or infected.
Other red flags include restlessness, difficulty sitting, or avoiding activities they usually enjoy. If your pet shows these signs, it’s time to consult a vet. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into serious health problems.
Guidelines for Preparing for a Vet Visit
Before visiting the vet, gather all relevant information about your dog’s symptoms. Note the frequency and duration of behaviors like scooting or licking. Document any changes in stool consistency or unusual odors.
During the appointment, communicate clearly with the vet. Provide a detailed history of your dog’s health and any recent changes in diet or behavior. This information helps the vet diagnose the problem accurately and recommend the best treatment.
“Timely veterinary care can save your dog from unnecessary pain and prevent complications.”
If your dog shows sudden changes in behavior or increased discomfort, seek professional help immediately. Proper treatment by a vet ensures your pet’s health and comfort. Early detection and action are key to maintaining your dog’s well-being.
Manual Expression Techniques
Properly managing your dog’s anal gland health is essential for their comfort and well-being. While many pets naturally express these glands during bowel movements, some require manual assistance. Understanding the correct techniques ensures your pet’s safety and prevents complications.
Home Expression: Precautions and Safety Tips
Before attempting gland expression at home, prepare the environment and gather necessary supplies. Wear latex gloves and use a water-based lubricant to minimize discomfort. Ensure your pet is calm and secure, as sudden movements can cause injury.
It’s crucial to avoid applying excessive pressure, which can lead to pain or damage. If your pet shows signs of distress, such as whining or struggling, stop immediately. Having a second person assist can help keep your dog steady during the process.
“Safety and hygiene are paramount when performing manual gland expression at home.”
Step-by-Step Guide to Expressing Anal Glands
Follow these steps to safely and effectively express your dog’s anal glands:
- Lift your dog’s tail gently to expose the anus.
- Apply lubricant to your gloved finger and insert it into the area at the 4 or 8 o’clock position.
- Locate the gland, which feels like a small, firm sac.
- Apply gentle pressure in a milking motion to release the fluid.
- Clean the area thoroughly with a damp cloth afterward.
If you notice blood, pus, or signs of pain during the process, consult your veterinarian immediately. These symptoms may indicate an infection or abscess requiring professional treatment.
Regular monitoring and proper technique can help maintain your dog’s gland health. By following these guidelines, you can ensure your pet remains comfortable and free from complications.
Treatment Options for Anal Gland Problems
Addressing anal gland issues in dogs requires a clear understanding of available treatment options. From medications to surgical interventions, each method aims to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications. Consulting a vet ensures the right approach for your pet’s specific needs.
Medication and Local Treatments Explained
Mild cases of gland problems often respond well to medications. Oral antibiotics help resolve infections, while anti-inflammatory drugs reduce pain and swelling. Topical ointments, applied directly to the affected area, can also provide relief.
Local treatments, such as manual expression, are commonly used to empty the sac. This procedure, performed by a vet, ensures the gland is cleared of buildup. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to prevent recurrence.
Surgical Interventions and Advanced Care
In severe cases, surgical removal of the gland may be necessary. This option is considered when recurrent infections or abscesses occur. While surgery is a last resort, it can provide long-term relief for chronic issues.
Post-surgical care involves pain management and monitoring for complications. Your vet will guide you through the recovery process, ensuring your pet’s comfort and well-being. Prompt treatment is key to preventing further complications.
“The right treatment plan, tailored to your dog’s needs, ensures a swift recovery and lasting health.”
Here’s a quick comparison of treatment methods:
- Medications: Effective for infections and inflammation.
- Manual Expression: Clears buildup in mild cases.
- Surgery: Recommended for chronic or severe issues.
By understanding these options, you can work with your vet to choose the best treatment for your dog’s gland problem. Early action ensures your pet remains happy and healthy.
Prevention and Dietary Considerations

Preventing anal gland issues in dogs starts with a proactive approach to their diet and overall health. By making informed choices about what your pet eats, you can reduce the risk of discomfort and complications. A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining proper gland function and preventing impaction.
The Role of High Fiber Diets in Gland Health
High-fiber foods are essential for promoting firm stools, which naturally express the anal glands during bowel movements. Ingredients like pumpkin, psyllium husk, and whole grains can help achieve this. Firm stools apply the necessary pressure to empty the glands, reducing the risk of buildup.
Food allergys can also contribute to inflammation, leading to gland problems. Identifying and eliminating allergens from your dog’s diet can prevent unnecessary discomfort. Regular reviews of your pet’s diet with a veterinarian ensure they receive the right nutrients for optimal health.
“A high-fiber diet can reduce the risk of anal gland issues by up to 50%, making it a key preventive measure.”
Maintaining a Healthy Weight for Your Dog
Excess weight can increase pressure on the anal glands, making it harder for them to function properly. Overweight dogs are more prone to gland problems due to weaker muscles around the anus. Regular exercise and portion control are essential for maintaining a healthy weight.
Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids can also support gland health. These anti-inflammatory nutrients help reduce swelling and promote overall well-being. Including fish oil or flaxseed in your pet’s diet can provide these benefits.
Here are some actionable tips for preventing gland issues:
- Choose high-fiber foods to promote firm stools.
- Monitor for food allergys and adjust the diet accordingly.
- Ensure your dog maintains a healthy weight through exercise and balanced meals.
- Consult your veterinarian for routine diet reviews and supplements.
By focusing on prevention, you can save your pet from unnecessary pain and costly treatments. A proactive approach to diet and health ensures your dog remains happy and comfortable.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing gland issues early is essential for your pet’s comfort and health. The natural process of gland expression during bowel movements can sometimes fail, leading to discomfort or infection. Key signs like scooting, excessive licking, or a foul odor should prompt immediate attention.
Home techniques, such as manual expression, can help, but professional veterinary care is often necessary for persistent problems. Treatments range from medications to surgical interventions, depending on the severity. Prevention plays a vital role—maintaining a high-fiber diet and a healthy weight can reduce the risk of issues.
Regular monitoring of your pet’s anal area and behavior ensures early detection. If symptoms persist, consult a vet promptly. Proper management of gland health not only prevents discomfort but also enhances your pet’s overall well-being.
For more detailed guidance on managing gland issues, visit our comprehensive guide here. Taking proactive steps ensures your pet leads a happy, healthy life.




Isnt it wild how weve evolved to discussing our dogs anal glands in such depth? What a time to be alive!
This guide is super informative, but how often should I check my dogs anal glands? Any vets here with advice?